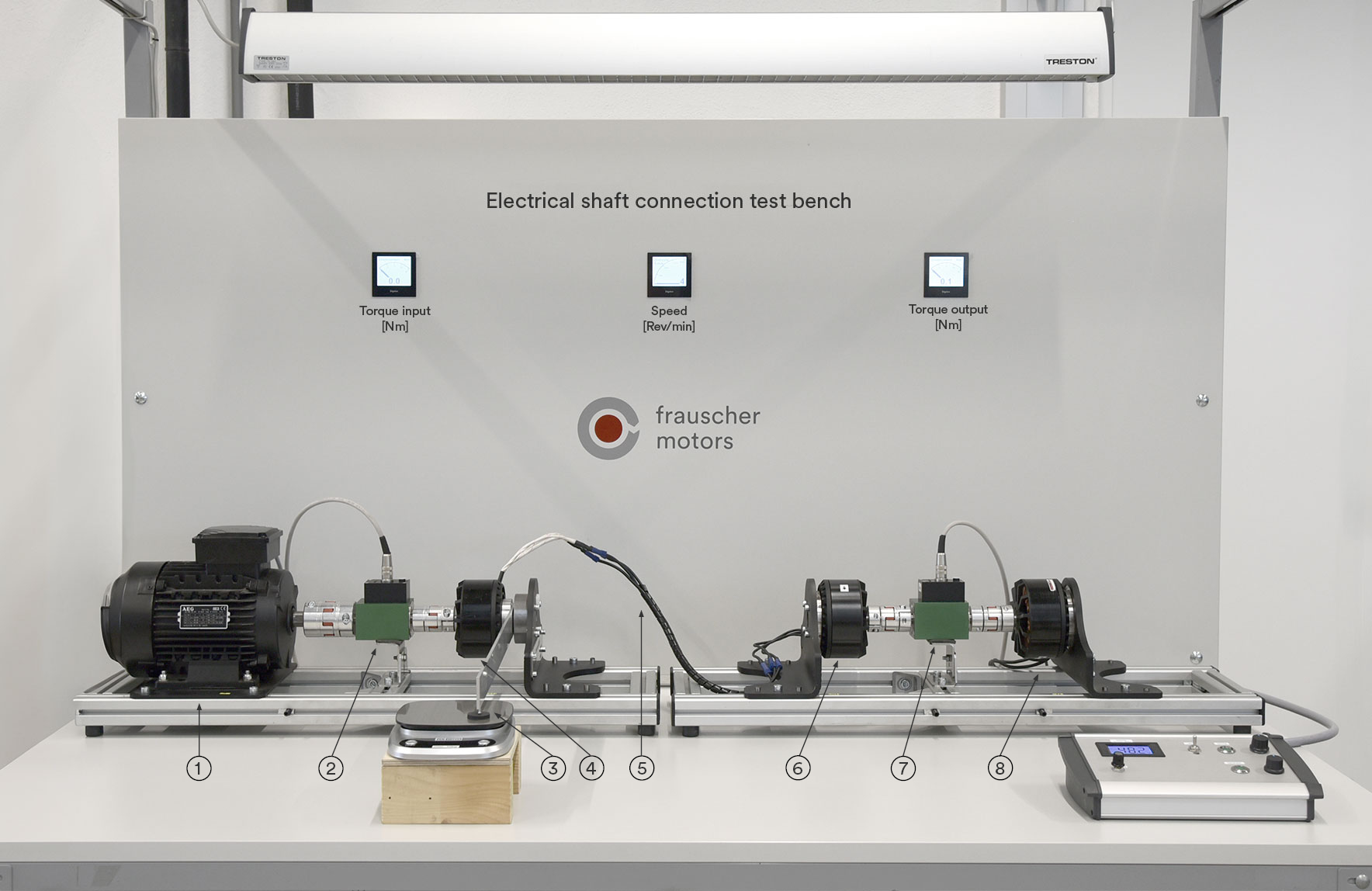
As part of their thesis, students Marlies Mairhofer and Konrad Niedermayr developed a remarkable demonstration system: a replica of the electromechanical energy chain that can be used, for example, for a hybrid drive in heat pumps. Shortly after its completion, the project was met with enthusiasm by our trade visitors.
The operating principle is easy to explain. When the three-wire three-phase connections of two identical electric synchronous machines are connected, the machines behave as if they were mechanically coupled via a shaft. When the first machine is driven, the second machine rotates at the same speed and in the same direction. The transmissible torque extends to the load limit of each individual machine and the efficiency far exceeds the values that can be achieved with transmission via a DC intermediate circuit using an inverter.
Frauscher Motors is therefore able to operate the compressor of a heat pump with Stirling generators. Since the Stirling engine drives the generator with constant torque, the expansion valve of the heat pump controls the speed of the compressor and, consequently, the thermal output of the heater.
But that’s not all: Since these are electrically switchable connections, the heat pump can still be operated from the house network via an inverter, for example when sufficient PV or wind power is available. If there is no heat demand, the Stirling generator can supply its energy to the house network or to a storage battery. This provides flexibility and self-sufficiency in the case of stand-alone solutions or power failures.
It has been proven that even with a COP of 4, the heat pump can achieve fuel savings of around 40% for the heating system. The cooling heat from the Stirling engine is used to reduce the temperature difference in the heat pump circuit. For more information, please refer to our data sheet.
Device designations:
- Drive motor (Stirling engine simulation)
- Torque measurement
- Torque control (balance)
- Synchronous generator of the Stirling engine
- 3-phase line connection
- Synchronous motor of the heat pump
- Torque measurement
- Load simulation scroll compressor